AI Agents
- Home
- AI Agents

// ABOUT AI Agents
AI Agents
AI agents go beyond task automation they pursue goals, adapt to change, and learn continuously. They bring intelligence and autonomy to every part of the enterprise.










What are AI agents?
AI agents are autonomous digital tools powered by generative AI and large language models (LLMs). Instead of following detailed instructions, they work toward broader goals, making real-time decisions and taking action with minimal human input.
These agents interact naturally with users, manage complex tasks across systems, and can even be built using no-code platforms making them accessible to business teams. Whether handling customer queries or coordinating operations, AI agents add agility, speed, and intelligence to modern workflows.
Key Benefits of Modern AI Agents
Smarter Decision-Making at Speed
AI agents analyze massive datasets in real time, offering quick insights that help teams respond faster and with greater accuracy. This reduces delays in action and supports better, data-driven decisions.
Scalable, Personalized Customer Interactions
AI agents deliver instant, tailored responses across channels by learning from past interactions. They reduce wait times and support high volumes without sacrificing personalization or quality.
Continuous Learning for Ongoing Efficiency
Powered by machine learning, AI agents improve over time by learning from every task. This makes them more efficient, accurate, and aligned with business goals the longer they operate.
Continuous Learning for Ongoing Efficiency
Powered by machine learning, AI agents improve over time by learning from every task. This makes them more efficient, accurate, and aligned with business goals the longer they operate.
How do AI agents work?
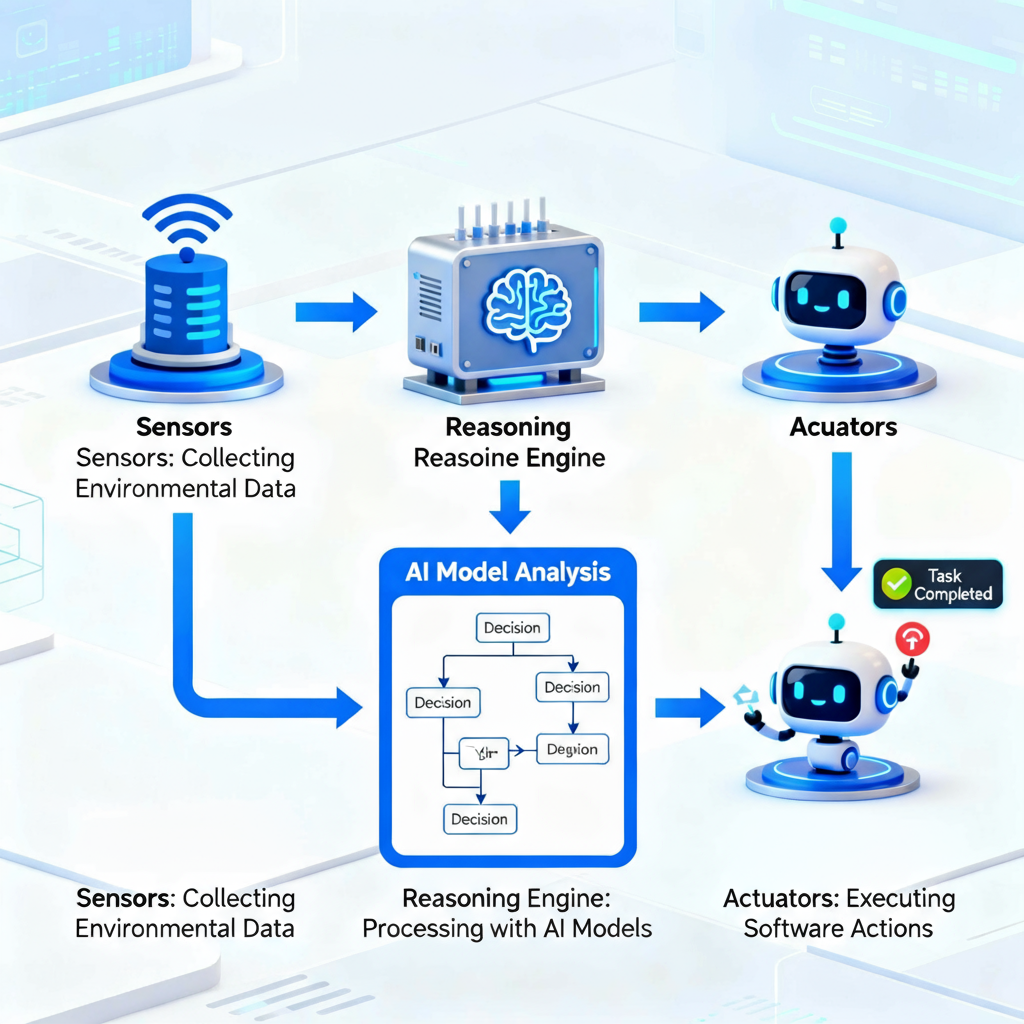
AI agents operate using three core components- sensors, a reasoning engine, and actuators. Sensors act as the agent’s input system, collecting structured and unstructured data from various sources like APIs, documents, or physical devices. This data provides the agent with context about its environment and tasks.
The reasoning engine processes this data, making decisions using machine learning and AI models. It evaluates patterns, predicts outcomes, and determines the best action to take. Once a decision is made, actuators often software bots carry it out. These might involve sending messages, updating systems, or executing business tasks. Together, these components allow agents to work independently and intelligently within complex systems.
How AI Agents Power the Agentic Ecosystem
AI agents are core to the intelligent automation ecosystem, working seamlessly with both humans and automation technologies to enhance productivity. Intelligent automation tools handle routine, repetitive tasks with consistency, while AI agents take on more strategic, adaptive roles that involve goal-setting and real-time decisions.
Humans remain essential providing oversight, handling exceptions, and making complex judgments when needed. This partnership between humans, AI agents, and intelligent automation systems results in streamlined operations where each component plays to its strengths.

We’re Here to Assist You and Address
All Your Questions Anytime!
AI Agent Use Cases Across New Industries
AI agents are unlocking new opportunities across industries by automating complex tasks, improving accuracy, and driving smarter decision-making.
HR Intelligence
Healthcare
Finance and Banking

Human Resources & People Teams
Intelligent agents assist with candidate screening, onboarding, and workforce analytics. Enhancing hiring efficiency and employee experience with data-driven insights.

Healthcare Providers & Admins
AI agents support diagnostics, automate admin tasks, and monitor patient vitals – helping deliver faster, more personalized care while reducing operational burdens.

Financial Services & Banking
AI agents detect fraud, assess risk, and deliver personalized financial insights by analyzing massive datasets in real time – boosting security, accuracy, and customer trust.
Types of AI Agents
Simple Reflex Agents
These agents act based on predefined rules and immediate input, without memory or learning. They respond directly to specific conditions (e.g., a thermostat turning off when it reaches a set temperature).
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, these have a basic internal model of the world. They use this model to track changes and make slightly more informed decisions based on both current input and previous states.
Utility-Based Agents
These agents not only aim for goals but also prioritize outcomes based on preferences or utility. They choose actions that maximize overall benefit, balancing trade-offs when goals conflict.
Learning Agents
These agents improve over time by learning from their experiences. They adjust their behavior through feedback loops, making them ideal for dynamic environments like customer service or fraud detection.
Multi-Agent Systems
These involve multiple AI agents working together (or competing), often with distributed goals. They’re used in complex systems like smart supply chains, traffic control, or collaborative robotics.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, these have a basic internal model of the world. They use this model to track changes and make slightly more informed decisions based on both current input and previous states.
Multi-Agent Systems
These involve multiple AI agents working together (or competing), often with distributed goals. They’re used in complex systems like smart supply chains, traffic control, or collaborative robotics.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, these have a basic internal model of the world. They use this model to track changes and make slightly more informed decisions based on both current input and previous states.
Challenges of AI Agents
AI agents offer powerful capabilities, but their success depends on overcoming key hurdles in ethics, integration, and technical performance.
The Future of AI Agents
AI agents are evolving rapidly, becoming smarter, more autonomous, and deeply integrated into business operations. With improvements in natural language processing and contextual understanding, these agents are moving beyond simple task automation to take on complex, multi-step responsibilities with minimal human input.
Looking ahead, AI agents will play a bigger role in transforming how businesses operate – from streamlining supply chains to delivering hyper-personalized customer experiences. As their decision-making and learning abilities advance, AI agents will shift from being tools to becoming trusted digital collaborators across industries.